02 Shoulder
typora-copy-images-to: ./images


Rotator Cuff

- holds shoulder together
- holds humerus head in place during abduction
Supraspinatus

- supra to spine of scapula

- beneath acromion process and above humeral head
- common in people who use shoulder a lot


A complete supraspinatus tear causes weakness of abduction, which can be appreciated in the drop arm test. In this test, the patient's arm is abducted above the head and the patient is asked to lower the arm slowly. With a complete tear, the patient will be unable to lower the arm smoothly and it will drop rapidly around mid-adduction. Although the supraspinatus is the primary muscle responsible for initiating the first 15 degrees of abduction, the loss of smooth adduction in the drop arm test typically occurs when the humerus is near the horizontal plane. MRI can confirm the diagnosis, and treatment usually requires surgery.
Infraspinatus


Teres Minor

- 6
Subscapularis


Movement


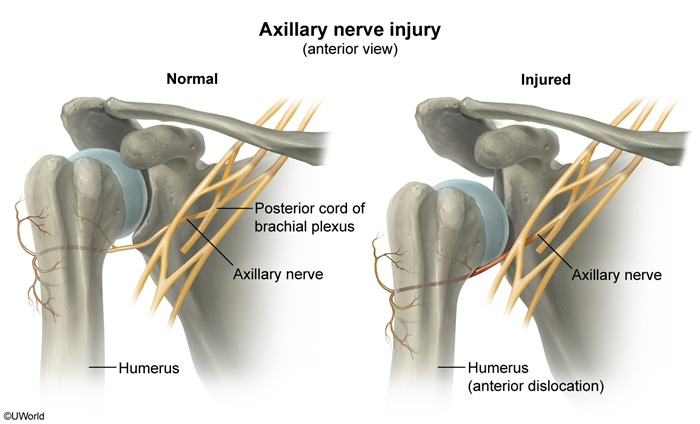
- humerus move out of glenoid fossa
- anterior dislocation: head moves anterior, front of joint
- The shoulder may dislocate anteriorly, inferiorly, or posteriorly, but anterior dislocations are by far the most common. Anterior dislocations are typically caused by a blow to an externally rotated and abducted arm.

Elbow

Epicondylitis

- main overuse injury



Radial Head Subluxation

- partial dislocation of head of radius bone
- commonly happens to children when yanked by nursemaids


- brachial artery: just above elbow joint

